The Tapestry of Life: Exploring the Importance and Threats to Biodiversity

Biodiversity, short for biological diversity, encompasses the variety of life on Earth at all its levels, from genes to ecosystems, and the ecological and evolutionary processes that sustain it. It’s the intricate web of interconnectedness that makes our planet habitable and provides us with essential resources and services. Understanding and protecting biodiversity is not just an environmental concern; it’s a fundamental imperative for human well-being and the future of our planet.
What is Biodiversity? A Deeper Dive
Biodiversity isn’t just about the number of different species. It’s a multifaceted concept that includes:
- Genetic Diversity: The variation of genes within a species. This allows populations to adapt to changing environments and resist diseases. A population with high genetic diversity is more resilient and less susceptible to extinction.
- Species Diversity: The variety of different species in a given area. This includes plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other organisms. Species diversity is often measured by the number of species (species richness) and their relative abundance (species evenness).
- Ecosystem Diversity: The variety of different habitats, ecological communities, and ecological processes. This includes forests, grasslands, wetlands, coral reefs, and deserts. Each ecosystem provides unique habitats and supports a different set of species.
These three levels are interconnected and interdependent. Genetic diversity within a species contributes to its ability to thrive in different ecosystems, and the interaction between different species within an ecosystem contributes to its overall health and stability.
The Importance of Biodiversity: An Ecosystem of Benefits

Biodiversity provides us with a vast array of benefits, often referred to as ecosystem services. These services are essential for human survival and well-being:
- Provisioning Services: These are the tangible products we obtain from ecosystems, including:
- Food: Biodiversity provides us with a wide range of food sources, from crops and livestock to fish and wild plants.
- Water: Healthy ecosystems regulate water cycles, ensuring clean and reliable water supplies. Forests act as natural sponges, absorbing rainfall and releasing it slowly, preventing floods and droughts.
- Medicinal Resources: Many medicines are derived from plants and animals. Biodiversity offers a vast untapped potential for discovering new treatments for diseases.
- Raw Materials: Ecosystems provide us with timber, fibers, and other raw materials used in construction, manufacturing, and other industries.

- Regulating Services: These services help regulate environmental conditions, including:

- Climate Regulation: Forests and oceans absorb carbon dioxide, helping to mitigate climate change. Wetlands act as carbon sinks, storing large amounts of carbon.
- Air and Water Purification: Plants filter pollutants from the air and water. Wetlands and mangroves act as natural filters, removing pollutants and improving water quality.
- Pollination: Insects, birds, and other animals pollinate crops and wild plants, ensuring food production and maintaining plant diversity.
- Disease Regulation: Biodiversity can help regulate the spread of diseases. For example, predators can control populations of disease-carrying rodents.
- Supporting Services: These are the fundamental ecological processes that support all other ecosystem services, including:
- Nutrient Cycling: Decomposers break down organic matter, releasing nutrients that are essential for plant growth.
- Soil Formation: Soil organisms contribute to the formation and maintenance of healthy soils, which are essential for agriculture and forestry.
- Primary Production: Plants convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, forming the base of the food chain.
- Cultural Services: These are the non-material benefits we obtain from ecosystems, including:
- Recreation and Tourism: Natural landscapes provide opportunities for recreation, tourism, and spiritual enrichment.
- Aesthetic Value: Biodiversity enhances the beauty of our surroundings and provides inspiration for art, music, and literature.
- Spiritual and Religious Significance: Many cultures have deep spiritual connections to nature and specific species.
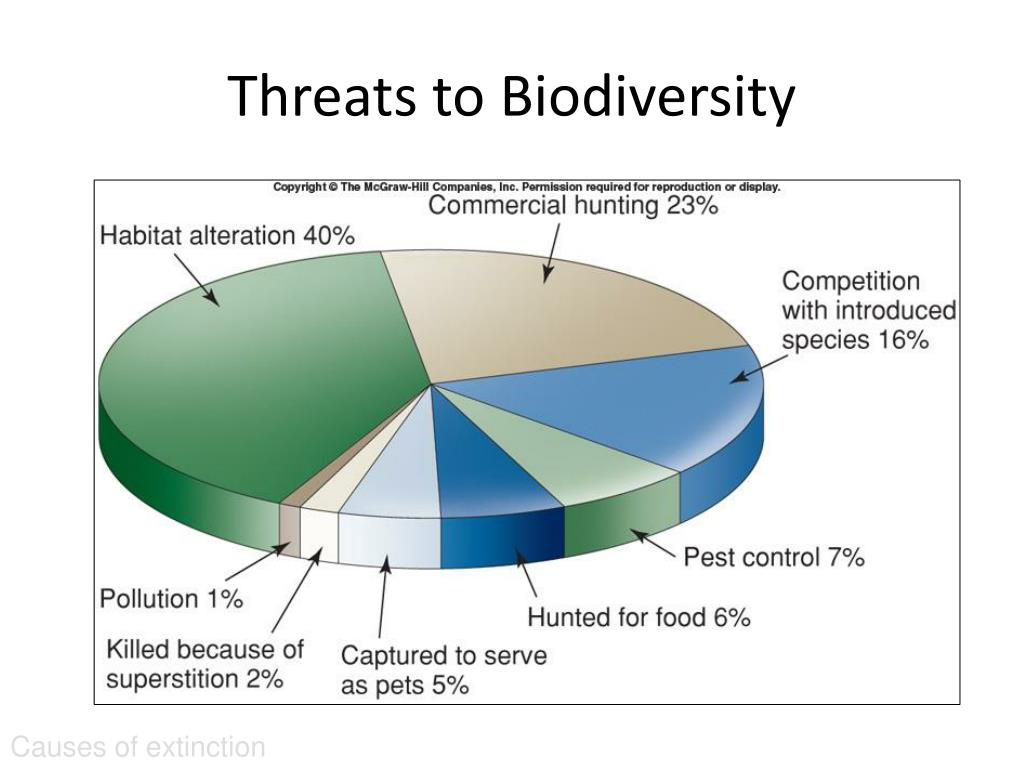
Threats to Biodiversity: A Looming Crisis
Unfortunately, biodiversity is under threat worldwide. Human activities are driving species extinctions at an unprecedented rate, far exceeding the natural background rate. The main threats to biodiversity include:
- Habitat Loss and Degradation: This is the most significant threat to biodiversity. As human populations grow, we convert natural habitats into agricultural land, urban areas, and industrial sites. Habitat fragmentation, where large habitats are broken up into smaller, isolated patches, also reduces biodiversity.
- Climate Change: Climate change is altering habitats, shifting species ranges, and disrupting ecological processes. Rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events are putting many species at risk.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, overhunting, and illegal wildlife trade are depleting populations of many species, particularly those that are slow-growing or have low reproductive rates.
- Pollution: Pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and urban runoff is contaminating air, water, and soil, harming wildlife and disrupting ecosystems.
- Invasive Species: Invasive species are non-native species that are introduced to new environments and outcompete native species for resources, causing ecological damage.
Conserving Biodiversity: A Call to Action
Conserving biodiversity requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the root causes of biodiversity loss. Some key strategies include:
- Protecting and Restoring Habitats: Establishing protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife reserves, is crucial for safeguarding biodiversity. Restoring degraded habitats, such as forests and wetlands, can also help to recover biodiversity.
- Promoting Sustainable Agriculture and Forestry: Sustainable agricultural and forestry practices can reduce the negative impacts of these activities on biodiversity. This includes reducing the use of pesticides and fertilizers, promoting crop rotation, and practicing sustainable logging.
- Combating Climate Change: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is essential for mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity. This requires transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and protecting forests.
- Controlling Invasive Species: Preventing the introduction of invasive species and controlling their spread is crucial for protecting native biodiversity. This includes implementing quarantine measures, eradicating invasive species, and restoring native habitats.
- Raising Awareness and Education: Educating the public about the importance of biodiversity and the threats it faces is essential for promoting conservation efforts. This includes providing information about sustainable practices and encouraging people to take action to protect biodiversity.
- International Cooperation: Biodiversity conservation requires international cooperation, as many species migrate across national boundaries and many threats to biodiversity are global in scope. This includes implementing international agreements on biodiversity conservation and promoting sustainable development.
The Future of Biodiversity: A Choice We Must Make
The future of biodiversity is uncertain, but it is not too late to take action. By addressing the threats to biodiversity and implementing effective conservation strategies, we can protect the tapestry of life on Earth and ensure a sustainable future for ourselves and future generations. The choice is ours. We can continue down the path of biodiversity loss, or we can choose to protect the natural world and secure a healthy and vibrant planet for all.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between conservation and preservation?
A: Conservation focuses on the sustainable use and management of natural resources, ensuring that they are available for future generations. Preservation, on the other hand, aims to protect natural areas from any human disturbance, allowing them to remain in their pristine state.
Q: How can I contribute to biodiversity conservation in my daily life?
A: There are many ways to contribute to biodiversity conservation, including:
- Reducing your carbon footprint by using public transportation, biking, or walking.
- Conserving water and energy.
- Buying sustainable products.
- Supporting organizations that are working to protect biodiversity.
- Planting native trees and plants in your garden.
- Avoiding the use of pesticides and herbicides.
- Educating yourself and others about biodiversity.
Q: What is the role of governments in biodiversity conservation?
A: Governments play a crucial role in biodiversity conservation by:
- Establishing protected areas.
- Enacting and enforcing environmental laws.
- Promoting sustainable development.
- Investing in research and monitoring.
- Raising public awareness.
- Participating in international agreements.
Q: What are the economic benefits of biodiversity conservation?
A: Biodiversity conservation provides numerous economic benefits, including:
- Supporting tourism and recreation.
- Providing ecosystem services that are essential for agriculture and forestry.
- Providing raw materials for industries.
- Reducing the costs of disaster relief.
- Creating new economic opportunities in sustainable industries.
Q: Is it possible to reverse biodiversity loss?
A: While some species extinctions are irreversible, it is possible to reverse biodiversity loss in many cases by implementing effective conservation strategies. This requires addressing the root causes of biodiversity loss, such as habitat loss, climate change, and pollution, and restoring degraded ecosystems.
Conclusion
Biodiversity is the foundation of a healthy planet and a prosperous future for humanity. The intricate web of life provides us with essential resources, regulates environmental conditions, and enriches our lives in countless ways. However, human activities are driving biodiversity loss at an alarming rate, threatening the stability of ecosystems and the well-being of future generations. By understanding the importance of biodiversity and taking action to protect it, we can ensure a sustainable future for ourselves and all living things. The time to act is now, before it is too late to reverse the damage we have caused. Let us work together to conserve the tapestry of life and safeguard the future of our planet.